Family, Health & Lifestyle
A guide to smoking: its causes, complications, and treatment
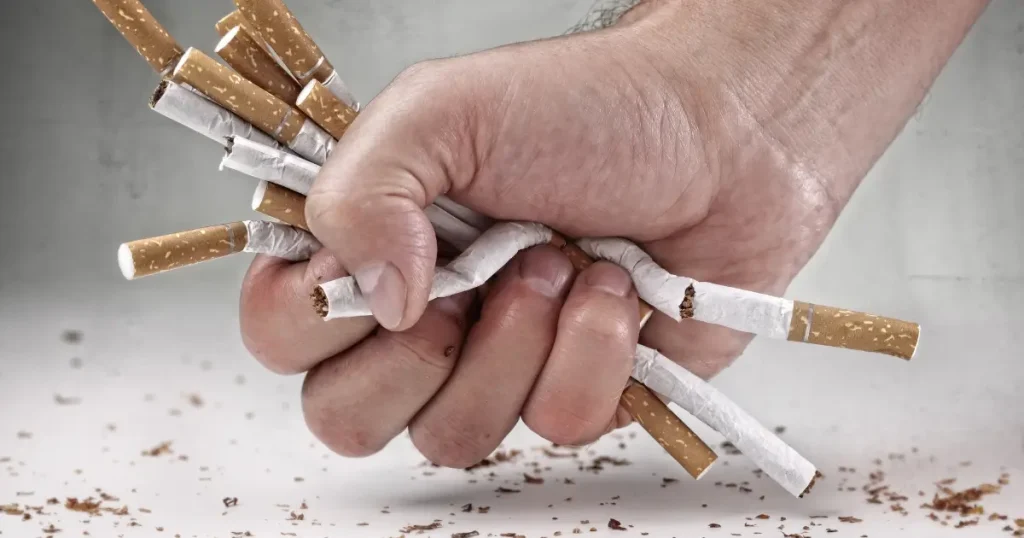
Smoking tobacco damages almost all of the body’s organs.
It elevates the likelihood of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, heart attacks, and other conditions.
Nicotine is an addictive substance that is present in tobacco.
During the withdrawal period, individuals who discontinue their nicotine use may experience anxiety, sorrow, restlessness, and irritability.
Nicotine is the substance in tobacco (including cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, and e-cigarettes) that consumers become addicted to.
In addition to nicotine, cigarettes contain tar and carbon monoxide, as well as approximately 4,000 other constituents, many of which are toxic.
Certain pharmaceutical products also include nicotine as an active constituent to aid individuals in quitting smoking.
Nicotine is highly addictive due to its rapid delivery to the brain (within 10 seconds) when an individual inhales cigarettes.
A transdermal patch provides a non-addictive, consistent, and gradual delivery of nicotine.
Guide to smoking and its harms

Smoking tobacco is the primary source of nicotine exposure, although minors may unintentionally consume it (typically through cigarettes or cigarette butts left in ashtrays, or occasionally through nicotine gum, patches, or e-cigarette liquid). Additionally, some individuals use smokeless tobacco. Smoke. Most consumers use cigarettes, while a smaller proportion use cigars and pipes.
In the United States and globally, cigarette smoking continues to be the most prevalent cause of preventable disease and mortality. A smoking-related disorder will result in the premature death of approximately two out of every three individuals who smoke for an extended period.
Every year, over half a million Americans succumb to a tobacco-related disease, which is equivalent to one in every five fatalities in the United States.
tabac is fatal due to the inhalation of hundreds of substances, many of which are capable of causing cancer, heart disease, and lung disease. Even odorless tobacco products are not a secure alternative to smoking because they contain toxins.
Another hazard is that smoking is the most prevalent cause of unintentional home fires in the United States. Approximately 7,600 smoking-related fires occur in residential buildings annually, resulting in approximately 365 fatalities, 925 injuries, and a $326 million property loss, according to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).
In contrast to the mid-1960s, when one in two men and one in three women were smokers, approximately 14% of adults in the United States currently inhale cigarettes. Nevertheless, the absolute number of smokers in the United States has remained constant as a result of population growth.
There are about 35 million adults. Marketers primarily target teenagers and adults when selling cigarettes. Each day, approximately 1,600 adolescents under the age of 18 smoke their first cigarette, and approximately 200 of them become smokers.
Signs and symptoms
Smoking damages the majority of the body’s organs.
Immediate consequences
Nicotine is a stimulant that activates the reward center in the brain. Nicotine, when obtained through smoking, has the potential to increase vitality and concentration, as well as reduce appetite. Smoking may reduce the symptoms of nicotine withdrawal and provide a sense of relaxation once an addiction has developed. Unaccustomed to nicotine, individuals may experience flushing, nausea, or both.
Individuals employed in tobacco cultivation or processing and exposed to significant quantities of tobacco leaves may absorb nicotine through their skin. These individuals may experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, and weakness. This illness is called “green tobacco sickness.”
Children who consume tobacco products, nicotine gum, or e-cigarette liquid may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, fatigue, agitation, and confusion, sometimes as a result of a single cigarette. However, it is uncommon for minors to experience severe or fatal toxicity. This is partly due to the fact that vomiting causes the gastrointestinal contents to empty out.
Reasons
Nicotine is a chemical present in tobacco that exacerbates the difficulty of ceasing smoking. Nicotine enters the brain within seconds of inhalation.
The reward center of the brain releases dopamine, one of these neurotransmitters, which causes feelings of happiness and an improved mood.
As the number of cigarettes consumed increases, the amount of nicotine required to achieve a comfortable level of relaxation increases. Your daily routine quickly integrates nicotine, forming an association with your emotions and behaviors.
The following situations frequently trigger the urge to smoke:
- Consume coffee or take pauses during work hours.
- Engaging in telephone conversations
- Consuming alcohol
- Operating a vehicle
- Spend time with companions.
To overcome your nicotine addiction, it is essential to be cognizant of your triggers and devise a strategy to address them.
Risk variables
Addiction is a potential consequence of tabac or using other tobacco products. Various factors influence which group consumes tobacco.
the age. The majority of smokers initiate their smoking habits during their childhood or adolescent years. There is a greater likelihood of addiction when one begins smoking at a young age.
Factors of genetic origin. It is possible that your propensity to initiate and sustain smoking is partially genetic. Genetic factors may influence the response of receptors on the surface of nerve cells in the brain to high concentrations of nicotine delivered by cigarettes.
Peers and parents. Children raised by smoking parents are more likely to smoke themselves. Additionally, children who have peers who smoke are more inclined to experiment with it.
Depression, or any other mental illness. Numerous studies demonstrate a correlation between smoking and depression. Smoking is more prevalent among individuals who suffer from melancholy, schizophrenia, post-traumatic stress disorder, or other mental illnesses.
Alcohol and narcotic abuse. Smoking is more prevalent among individuals who consume alcohol and illicit substances.
Difficulties
Tobacco smoke contains over 60 chemicals known to cause cancer, as well as thousands of other hazardous substances. Harmful chemicals are present in even “all-natural” or medicinal cigarettes.
It is important to know that smokers are more likely to develop and die from certain diseases.
However, you are unaware of the numerous health issues that smoking itself induces.
Lung cancer and lung diseases. Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer-related deaths. Furthermore, smoking induces respiratory ailments, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Additionally, it worsens asthma.
Additional types of cancer exist.
Smoking increases the likelihood of developing numerous types of cancer, including those of the mouth, throat (pharynx), esophagus, larynx, bladder, pancreas, kidneys, cervix, and certain types of leukemia.
In general, smoking is responsible for 30% of all cancer-related fatalities.
Circulatory and cardiovascular disorders
elevates the risk of fatality from cardiovascular disease (CVD), which includes heart attacks and strokes.
Smoking may exacerbate the symptoms of heart or blood vessel disease, such as heart failure.
diabetic. Smoking may enhance insulin resistance, potentially facilitating the development of type 2 diabetes.
If you have diabetes, smoking may exacerbate complications, including kidney disease and eye issues.
Eye issues. It is possible to develop severe eye conditions, including macular degeneration and cataracts.
Impotence and infertility. Smoking increases the risk of impotence in men and decreased fertility in women.
Pregnancy complications.
Mothers who smoke during pregnancy are at increased risk of having premature infants and babies with lower birth weights.
Colds, influenza, and other ailments.
Respiratory infections, including influenza, bronchitis, and colds, are more prevalent among smokers.
Gum and tooth diseases.
Smoking increases the risk of gingivitis and severe periodontal infections, which can harm tooth support structures (periodontitis).
Smoking in close proximity to you also increases your susceptibility to health issues. Living with a smoker increases the risk of lung cancer and heart disease in nonsmokers. Additionally, children whose parents smoke are more susceptible to colds, ear infections, and exacerbated asthma.
Strategies for preventing
The following lines will provide an explanation of the various methods that contribute to smoking prevention and treatment:
Parents’ awareness of the negative effects of smoking is the most important factor in preventing smoking.
Parents closely monitor their children’s behavior during adolescence, which is the most perilous stage of life, as children frequently develop negative behaviors.
We provide educational institutions with information about the risks of smoking, especially the diseases linked to it.
The Ministry of Health must also present research on the diseases that result from smoking and how to prevent them, which plays a critical role in the fight against .
Furthermore, the Ministry of Youth and Sports is equally critical to the Ministry of Health, as sports are instrumental in preventing smoking. Consequently, it is imperative to prioritize youth centers and sports activities.
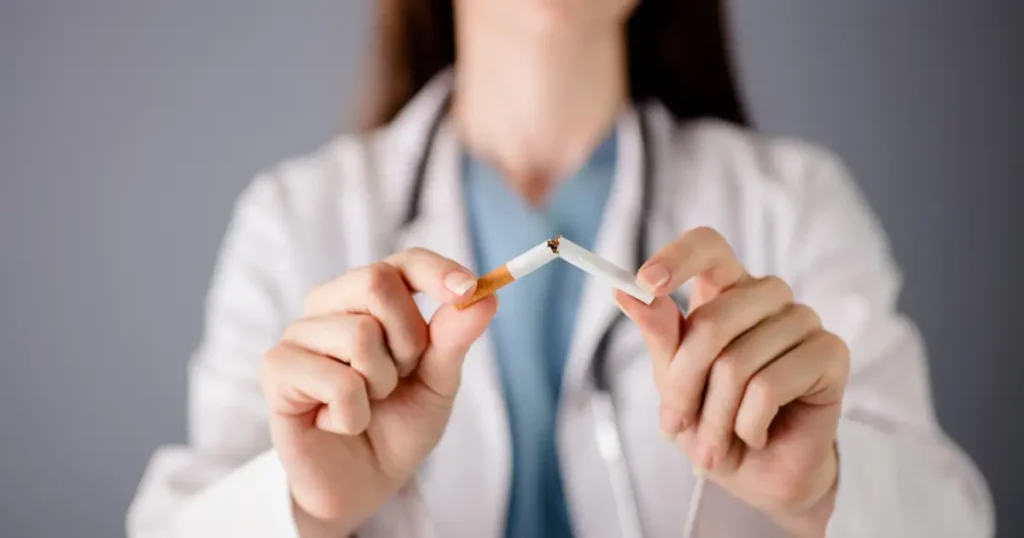
Smoking cessation therapies
- The following lines will explain smoking treatment methods as well as the harmful behaviors that an individual engages in.
- Parents are also responsible for preventing smoking. Additionally, they are responsible for its treatment, as parents must motivate their children to discontinue this detrimental behavior.
- Exercise is also essential for the recovery process . Therefore, individuals who wish to cease smoking should engage in physical activity and ensure that they maintain it.
- Furthermore, the individual who intends to cease smoking must adequately prepare for this challenge, as it requires robust willpower.
- Refraining from socializing with individuals who promote smoking can alleviate the individual’s smoking propensity.
- If you need nicotine, you can replace tobacco with stimulant beverages like tea and coffee.
In addition to the aforementioned, it may be beneficial to consult with a physician to eliminate this behavior.